The First Half of 2024: A Review of Data Breaches and Fraud
A review of data breaches, their impact, and key trends with a focus on major incidents, prevention tips, and case studies.
As 2024 progresses, the alarming frequency of data breaches continues to underscore the importance of cybersecurity. This article looks at the first half of the year, focusing on major breaches, their effects, and new strategies to reduce these risks.
Significant Data Breaches in 2024
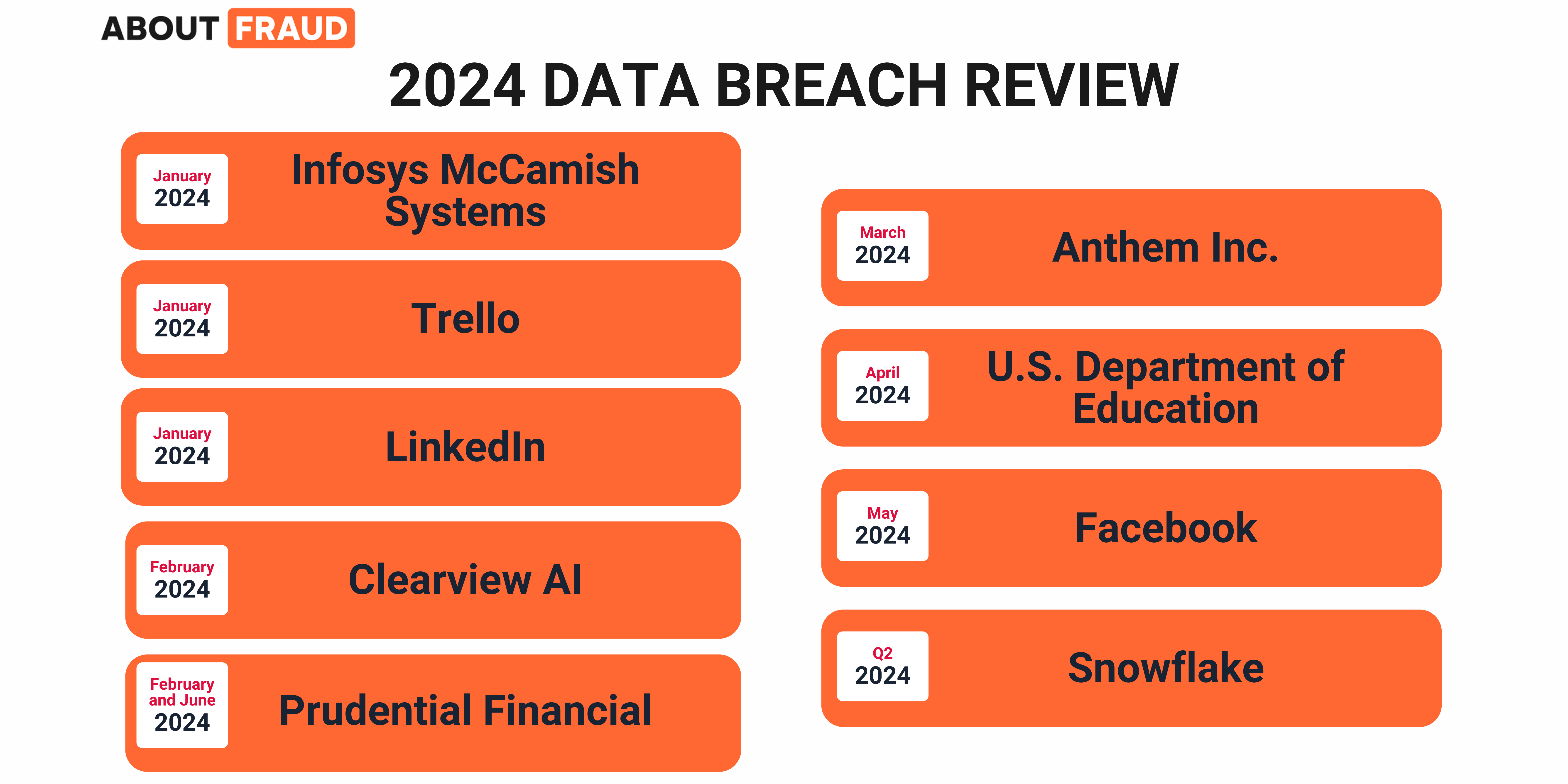
Infosys McCamish Systems (January 2024)
- Data Leaked: Initially 84,000, revised to 6 million
- Details: The breach involved sensitive information, and the scale was significantly revised upwards mid-year.
Trello Data Breach (January 2024)
- Data Leaked: 15 million users
- Details: User data, including email addresses and usernames, were leaked and put up for sale on a hacking forum.
LinkedIn (January 2024)
- Data Leaked: Over 500 million records
- Details: This breach exposed a massive number of user records, including email addresses, phone numbers, and other personal information. The information was harvested and listed for purchase on a the dark web.
Clearview AI (February 2024)
- Data Leaked: 4 million records
- Details: The breach exposed facial recognition data, including images and personal information, raising significant privacy concerns.
Prudential Financial (February & June 2024)
- Data Leaked: Initially 36,000, later revised to 2.5 million
- Details: This breach involved sensitive financial data and affected millions of individuals after an update in victim count.
Anthem Inc. (March 2024)
- Data Leaked: 10 million records
- Details: This breach was caused by a ransomware attack. It exposed sensitive healthcare information, including medical records and Social Security numbers.
U.S. Department of Education (April 2024)
- Data Leaked: 1.5 million records
- Details: A security breach exposed students’ and families’ financial details and Social Security numbers in the Federal Student Aid system.
Facebook (May 2024)
- Data Leaked: 1.2 million records
- Details: The breach resulted from a vulnerability in the platform’s API, exposing user data, including private messages and friend lists.
Snowflake Credential Stuffing Attack (Q2 2024)
- Data Leaked: Over 900 million records
- Details: This attack targeted customers of the Snowflake cloud service, making it one of the largest breaches of the year.
An Overview of Data Breaches in 2024
Data breaches have reached new highs in 2024. By mid-year, over 1.3 billion records were compromised (2024 Identity Breach Report by Constella Intelligence). Experts largely attribute this surge to increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks targeting numerous sectors, from healthcare to government agencies.
“The scale of data breaches in 2024 is a stark reminder that no organization is immune to cyber threats. The complexity and frequency of these breaches require a more robust and proactive approach to cybersecurity,” said Ray Devlin, CEO of Constella Intelligence.
The report highlights the rise of ransomware and phishing attacks by fraudsters. These attacks are now more targeted and effective and can cause serious problems for both individuals and organizations.
Key Points
The Volume of Breaches
In the first half of 2024, there was a worrying rise in data breaches. Healthcare and government agencies were the most affected. Hackread reports that a major breach involved the National Public Data Records (NPDR). Millions of sensitive records, including Social Security Numbers (SSNs), were leaked online.
“These breaches are not just numbers; they represent real people whose privacy and security are at risk,” stated Troy Hunt, a cybersecurity expert and founder of Have I Been Pwned. “The consequences for individuals can be devastating, leading to identity theft, financial loss, and long-term stress.”
Impact on Individuals and Organizations
The impact of these breaches extends far beyond financial losses. The 2024 Identity Breach Report says that the average cost of a data breach is now $4.5 million. This is a 15% increase from last year. This figure includes direct financial losses and costs from damage to brand reputation. It also covers the loss of customer trust and possible legal issues.
“Organizations must recognize that the true cost of a data breach is not just the immediate financial hit but the long-term impact on their reputation and customer relationships,” commented Eva Velasquez, President and CEO of the Identity Theft Resource Center.
Government and Legislative Response
In response to these growing threats, governments worldwide are stepping up efforts to enforce stricter cybersecurity regulations. In the U.S., new legislation aims to bolster cybersecurity defenses and increase penalties for non-compliance (see our article here), while the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) continues to impose heavy fines on organizations that fail to protect consumer data.
“Stronger regulations are essential, but they must be complemented by a genuine commitment from organizations to prioritize data security at every level,” noted Marietje Schaake, International Policy Director at Stanford University’s Cyber Policy Center.
Analysis of Major Breaches
National Public Data Breach
The breach of the National Public Data Records (NPDR) stands out as one of the most significant incidents in 2024. Millions of records, including SSNs, were dumped online, highlighting the vulnerabilities in government databases.
“This breach is a wake-up call for all government agencies. The exposure of such critical data not only endangers citizens but also undermines public trust in government institutions,” said Chris Vickery, Director of Cyber Risk Research at UpGuard.
Healthcare Sector Under Siege
The healthcare sector has been particularly vulnerable in 2024, with several high-profile breaches compromising patient data, including medical histories and insurance information. According to Constella’s report, healthcare breaches accounted for nearly 30% of all incidents in the first half of the year.
“The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals because of the sensitive nature of the data they hold. Unfortunately, many healthcare organizations are not equipped with the necessary resources to defend against these sophisticated attacks,” warned Larry Ponemon, Chairman and Founder of the Ponemon Institute.
Best Practice for Prevention
To mitigate the risk of data breaches, organizations must adopt proactive cybersecurity strategies. Here are some best practices:
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting routine audits helps identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks, allowing organizations to address them before they are exploited.
- Employee Training: Educating employees about phishing scams and other cyber threats is crucial in preventing breaches caused by human error.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it is compromised, it cannot be easily accessed or used by attackers.
- Incident Response Plan: Having a robust response plan in place enables organizations to act quickly and effectively in the event of a breach.
Case Studies and Examples
The Marriott International Breach
One of the notable breaches in 2018 was at Marriott International, where hackers gained access to customer data, including personal information and account numbers. This incident highlights the ongoing challenges faced by large corporations in securing vast amounts of customer data.
“Despite significant investments in cybersecurity, organizations like Marriott continue to face challenges in defending against persistent and sophisticated threats. It’s clear that more needs to be done to protect customer data,” commented Brian Krebs, a well-known cybersecurity journalist.
A Financial Institution’s Recovery Strategy
A leading financial institution successfully mitigated the impact of a potential breach through rapid response and transparent communication with affected customers. By offering credit monitoring services and enhancing security measures, the institution set an example of effective crisis management in the wake of a cyberattack.
To Conclude…
The first half of 2024 has been marked by a dramatic increase in data breaches, affecting millions worldwide. As cyber threats continue to evolve, it is imperative that organizations across all sectors prioritize cybersecurity. By implementing best practices, staying informed about the latest threats, and preparing for potential incidents, organizations can better protect themselves and their customers against fraud.
“The key to combating data breaches lies in vigilance, innovation, and collaboration across all sectors,” said Kevin Mandia, CEO of Mandiant.
The remainder of 2024 will undoubtedly bring new challenges, but with the right law enforcement strategies in place, the impact of data breaches can be mitigated.
| Tagged with: | fraud |
| Posted in: | AF Education |
